Diaphragmatic hernia
Problem
In congenital diaphragmatic hernia the diaphragm fails to close fully during embryonic development. During pregnancy abdominal organs such as the stomach, intestine, liver, and spleen can pass into the chest and restrict the growth of the lungs. In severe cases the lungs are so small that the newborn child cannot breathe and suffocates.
Diagnosis
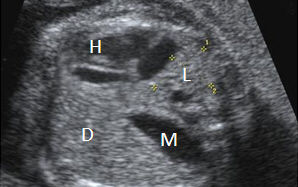
This malformation can be diagnosed by ultrasound. The adjacent image shows a cross-section through the chest. The heart (H) has been pushed far to the right by the stomach (S) and the intestine (I). The lungs (L) are small and compressed.
Therapy
Most affected children have a good prognosis because their lungs remain large enough.
In other cases the compressed lungs are so small that the fetus will die without prenatal intervention. In such cases we send the pregnant woman to our partner unit in Leuven, Belgium, where they use endoscopy to insert a balloon that closes the fetal trachea for several weeks. This strongly promotes lung growth and increases the survival rate considerably.
Outcome
The prognosis varies greatly and depends on the size of the fetal lungs. At our Center about two-thirds of affected children survive.
Publications
Fetal endoscopic tracheal occlusion (‘Fetendo-PLUG’) for congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
Skarsgard ED, Meuli M, VanderWall KJ, Bealer JF, Adzick NS, Harrison MR.J Pediatr Surg. 1996 Oct;31(10):1335-8. PubMed PMID: 8906656.
Fetal endoscopic (‘Fetendo’) tracheal clip.
VanderWall KJ, Bruch SW, Meuli M, Kohl T, Szabo Z, Adzick NS, Harrison MR.J Pediatr Surg. 1996 Aug;31(8):1101-3; discussion 1103-4. PubMed PMID: 8863243.
Fetal endoscopic (‘Fetendo’) surgery: the relationship between insufflating pressure and the fetoplacental circulation.
Skarsgard ED, Bealer JF, Meuli M, Adzick NS, Harrison MR.J Pediatr Surg. 1995 Aug;30(8):1165-8. PubMed PMID: 7472974.
The ‘PLUG’ odyssey: adventures in experimental fetal tracheal occlusion.
Bealer JF, Skarsgard ED, Hedrick MH, Meuli M, VanderWall KJ, Flake AW, Adzick NS, Harrison MR.J Pediatr Surg. 1995 Feb;30(2):361-4; discussion 364-5. PubMed PMID:7738765.