Spina bifida
Problem
During embryonic development the medullary plate closes two weeks after ovulation to form a tube which is then gradually enclosed by the protective spinal column. Should this step fail to occur at any point along the column, these extremely fragile structures acquire no external coating at that point and as a result are progressively damaged by amniotic fluid and mechanical contact with the uterine wall (1). At 24 weeks of pregnancy the spinal cord is often still intact (2). But once damage occurs there is no way of curing the severe neurological disability that follows. The end result is a form of paraplegia, often accompanied by hydrocephalus. Prompt investigation and counseling about possible prenatal surgery are therefore essential.
Diagnosis
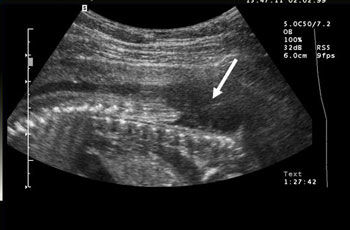
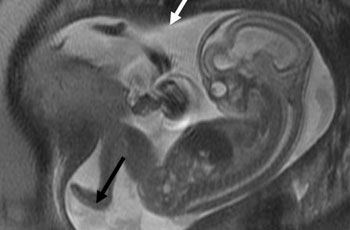
In almost all cases this severe malformation is diagnosed by ultrasound, which shows an absence of soft tissue over the spinal cord (1). An MRI scan can show the anatomical relationships in more detail and must always be performed if a prenatal operation is being considered (2). The MRI image also clearly shows the dilated cerebral ventricles (black arrow), indicative of hydrocephalus.
Therapy
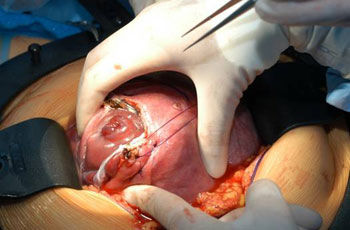
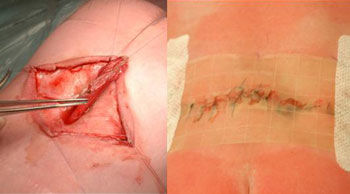
The standard treatment for a defect that has not been closed by fetal surgery is closure within a few days after birth. Unfortunately, this has no influence on the paralysis, as the neurological damage has already been done. Since 2011 prenatal, i.e. fetal, surgery has offered the possibility of a significant improvement in both the paralysis and the hydrocephalus. A fetal operation is therefore an important alternative to an operation after birth. Our Center offers this possibility and has already performed many successful prenatal operations for spina bifida.
Outcome
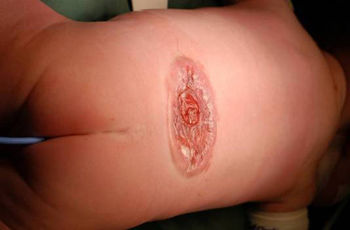
After a postnatal operation the child must expect to remain paralyzed for life below the open site on its back; in many cases it will also have hydrocephalus and need treatment for it, be wheelchair-bound, suffer from disorders of bladder and sexual function, and have severe back problems (1). Children who are operated on prenatally can expect significantly less disability.